MODALITIES
ACUPUNCTURE
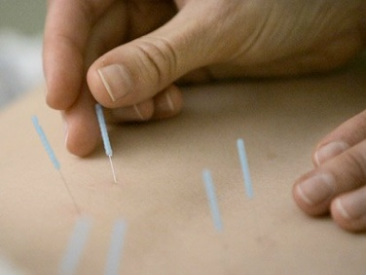
Acupuncture is the insertion of very fine needles in specific points of the body. Research has found evidence that acupuncture points are strategic conductors of electromagnetic signals. Stimulating points along the meridian enables these electromagnetic signals to be relayed at a greater rate than under normal.
Unlike hypodermic needles, acupuncture needles are ultra fine like a cat's whisker or a little larger than a human hair, and depending on the location, are usually painless. You may feel some heaviness, distention, heat, tingling, or electric sensation either around the needle or traveling up or down the affected meridian. However, you should feel relaxed during and after treatment. California law Section 1399.454 requires acupuncturists to use only sterile needles labeled for single use. It is unlawful to reuse acupuncture needles. This makes acupuncture a very safe modality with little danger of infection, and no side effects.
The World Health Organization recognizes acupuncture's effectiveness for over 40 common disorders (ENT, Respiratory, Gastrointestinal, Circulatory, Urogenital, Gynecological, Musculoskeletal, Psychoemotional & Neurological).
Acupuncture originated in China but spread to other countries where different styles were developed based on differing opinions of theory and technique. Therefore, the style of the acupuncturist will have an effect on the patient's comfort. You should speak with your acupuncturist about their particular style to determine whether that practitioner is right for you.
ELECTRO-ACUPUNCTURE

Electroacupuncture is the use of electric impulse stimulation through the acupuncture needles in affected areas and is utilized in pain related conditions, analgesia, labor induction, regeneration of nerve fibers and substance abuse. This type of treatment enhances the therapeutic effects of acupuncture. It is a pain-free procedure with a small amount of vibration in the affected area. There are two types of current, milliamp and microcurrent. Research has shown that milliamp is more effective for the release of endorphins to counteract pain, and microcurrent is more beneficial for tissue repair by causing cells to synthesize ATP at a higher rate.
CUPPING

Cupping is a treatment technique designed to stimulate the flow of blood and Qi within the superficial muscle layers. It is used for sore muscles, tension, neck pain, and for treating the common cold by breaking up phlegm in the chest and releasing stagnation. It involves the application of glass cups with heat to create suction, thereby pulling heat or toxins out of the body while stimulating local blood circulation. They may be moved over an affected area or left in place. The use of cups can cause redness and bruising which is considered part of the healing process.
GUA SHA

Gua Sha is another technique used to release muscle tension, tightness, and constriction. The patient may experience immediate relief from pain, stiffness, fever, chill, cough, or nausea. It is also valuable for the prevention of acute infectious illness, upper respiratory, or digestive problems. A specialized tool is used to gently scrape or rub the skin over a problem area for cutaneous stimulation that results in the appearance of small red petechiae similar to a bruise. This usually fades in two to three days.
